Direct Microscopy Observation of Mucormycosis (Black Fungus)
- One Method of Histology Diagnose of Mucormycosis Disease
People infected with COVID-19 are killed by the infection of Mucor from the environment. The fungal infection is spreading in India, where the new crown is rampant. According to the report from ‘Times of India’, the Indian government urged the States to declare the disease ‘epidemic’ on May 20, 2021.
What is mucormycosis?
Mucormycosis is a group of fungal infections caused by fungi. These fungi belong to Mucor, formerly known as Zygomycetes. The most common manifestation was rhino orbital brain infection, followed by lung, skin, disseminated and gastrointestinal infections. Mucormycosis is a common pathogenic factor in the soil, which can be found in rotten organic matter, such as bread, hay, and vegetation. The most common way of infection is through inhalation, but it can also be infected through the skin and subcutaneous inoculation.
The key of early diagnosis is to suspect the degree of potential immunosuppressive diseases. Identify the signs and symptoms, supportive imaging, histopathology, and culture of the involved tissues. For the patients who are suspected to be positive in combination culture, the microscope is one of the most direct tools to observe the pathological tissues and confirm the species of fungi.
What is kind of microscope can be used to diagnose fungus?
MSHOT is a professional application solution provider and manufacturer of fluorescence microscopes, which has been serving medical institutions and diagnostic enterprises for a long time. It has matured in vitro diagnosis programs experience and products in the field of dermatomycology diagnosis. Combined with the application experience of the fungal pathological diagnosis microscope and the sample processing method of Mucor, the following information can be referred to.
How microscope observe fungus?
According to the observation method of the microscope, it can be divided into two observation modes of bright field and fluorescence.
Ⅰ.Bright field micro-observation
PAS and GMS are commonly used in the field of Trichoderma. Under the magnification of 200X or 400X, the undivided/septated vesicles and banded hyphae (width of 10 – 20μ M) can be observed in tissue samples.
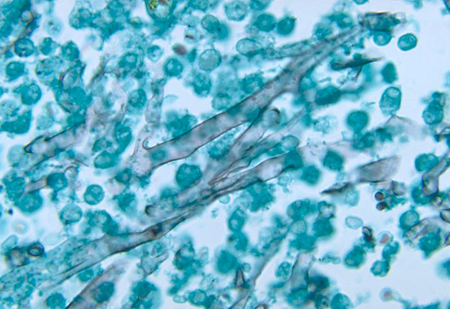
Hexamine silver staining showed sparse septate hyphae of Mucor minimus, selected from CDC public health image library (Phill): Dr. libero Ajello
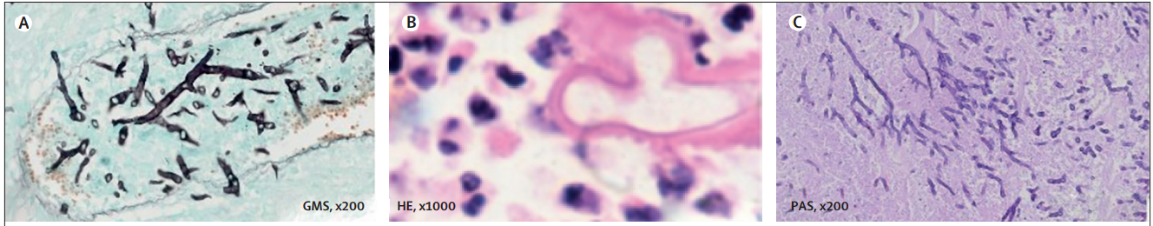
(A) Mucilaginous hyphae of mucormycosis lesions (typical hyphal morphology of GMS staining, 200 times magnification) were at least 6 – 16 µ M wide, banded, septate, irregularly branched.
(B) The structure of mycelium was enveloped by the phenomenon of Splendore hoeppli (HE staining, 1000 times magnification). Eosinophils may represent antigen-antibody complexes.
(C) Typical morphology of hyphenated aspergillosis (PAS staining, 200 magnification). The hyphae of Aspergillus are 3-5 µm wide, septum regular. Regularly bifurcated.
Photo A-C by Henrik E Jensen, cited from the European Union of Medical Mycology (EMCC) www.ecmm.info Website public information
Ⅱ. Fluorescence micro-observation
Fluorescence can be observed under a fluorescence microscope by staining tissue samples with fluorescent antigens.
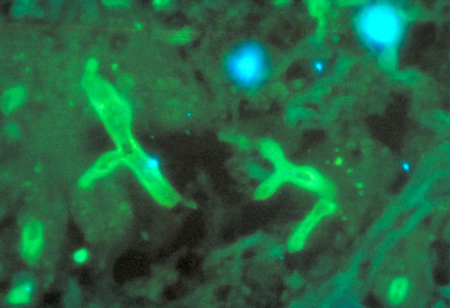
The fluorescence antigen stained Rhizopus rhizoids was selected from the CDC public health image library (Phil): Dr. William Kaplan
Another common fluorescence dye is Calcofluor white, which is a non-specific dye commonly used to detect fungi, yeast and other microorganisms. It has a very wide excitation spectrum and emission spectrum. Therefore, any filter with UV, Violet, or Blue excitation wavelength will generate fluorescence emission, which can be detected in a very wide range. Therefore, the selection of fluorescence light source and fluorescence filter is subjective, which depends on the preference and experience of microscope users.
The commonly used excitation wavelengths of Calcofluor white for Mucor dyeing are 365 ~ 380nm and 395 ~ 410nm. The models with UV excitation and fluorescence filter or Violet excitation and fluorescence filter in the configuration of fluorescence microscope can be used for observation.

(D -F ) The size and branching angle of myxomycetes and Aspergillus were stained by Calcofluor white. D and F are Rhizopus apetalus, e is Aspergillus fumigatus. The diameter of mycelium was observed and photographed by microscope and measured by Leica LAS-AF software.
Specific diagnosis needs to be confirmed by culture or molecular technology.
Image D-F by Ana Alastruey Izquierdo, cited from EMCC www.ecmm.info Website public information
What is brand and model fluorescence microscope can used for fungus observation?
The LED epi-fluorescence microscope MF31 produced by the MSHOT microscope manufacturer can realize the above two observation modes of bright field and fluorescence. This microscope can select different fluorescence excitation light sources and filter colors according to the actual application of fluorescein, such as 365 ~ 380nm and 395 ~ 410nm required by Calcofluor white; The 460 ~ 490 nm excitation light and filter are needed for fluorescence antigen staining, and three kinds of bands can be observed by one microscope.
Combined with MSHOT manufacutred microscope camera, it can take photos, measure, real-time and time-lapse imaging, record and analyze microscope images, and connect with a computer to print pictures.


(G) (H)
MF31 LED epi-fluorescence microscope and MSHOT microscope camera
Picture G is single-band fluorescence excitation model
Picture H is a multi-excitation fluorescence band model
Here are the photos of the microscope used in observing fungi and immunofluorescence

(I)Observation of skin fungal section UV light source and filter
(J) Fungal hyphae treated with fungal reagent dyes

(K) Immunofluorescence
What is fungis looks like under fluorescence microscope?
There are different types of fungi in the natural environment, including in organic matter, food, pets, and the human body. Here are some types of fungi observed and photographed by this microscope:
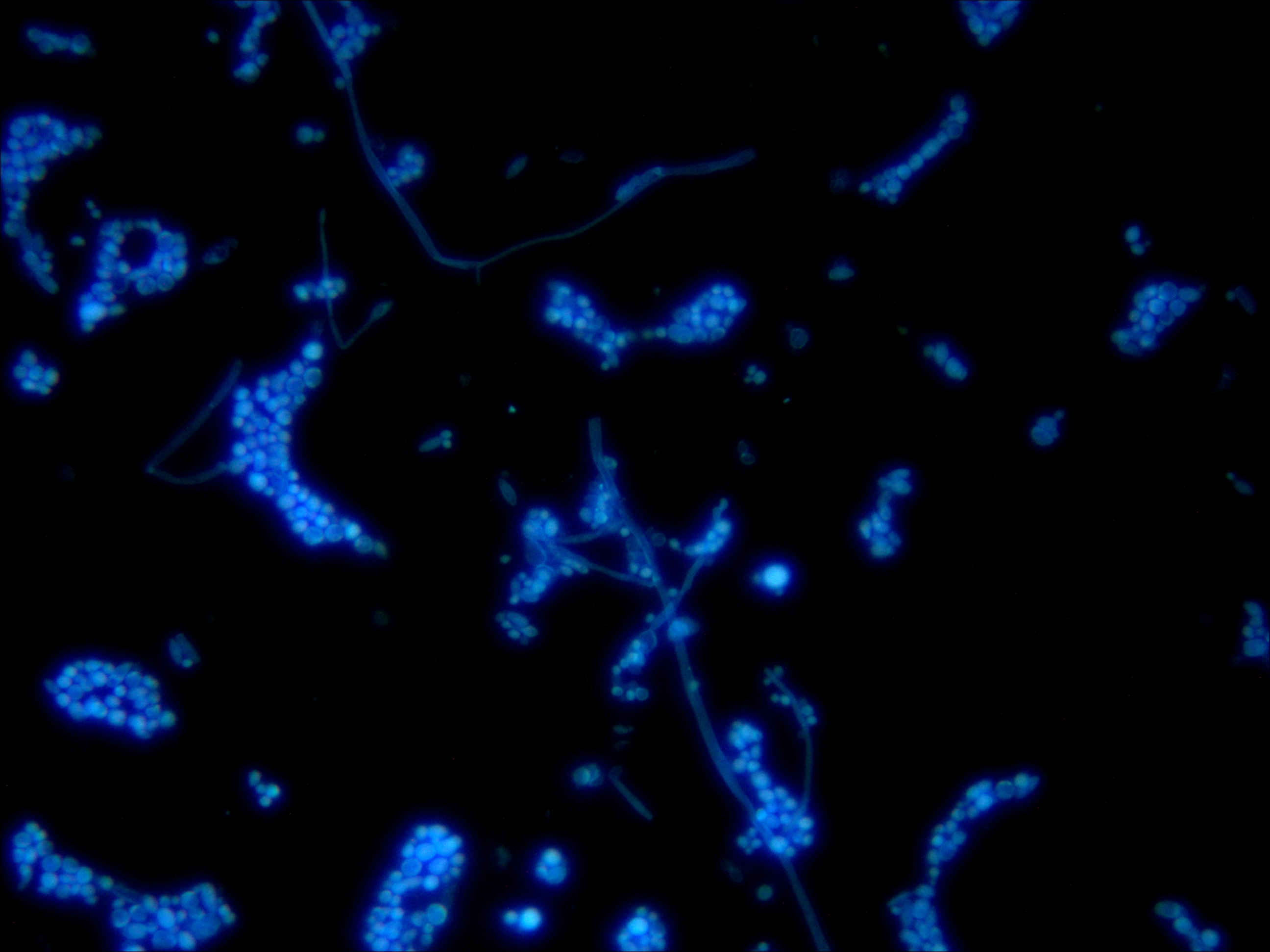
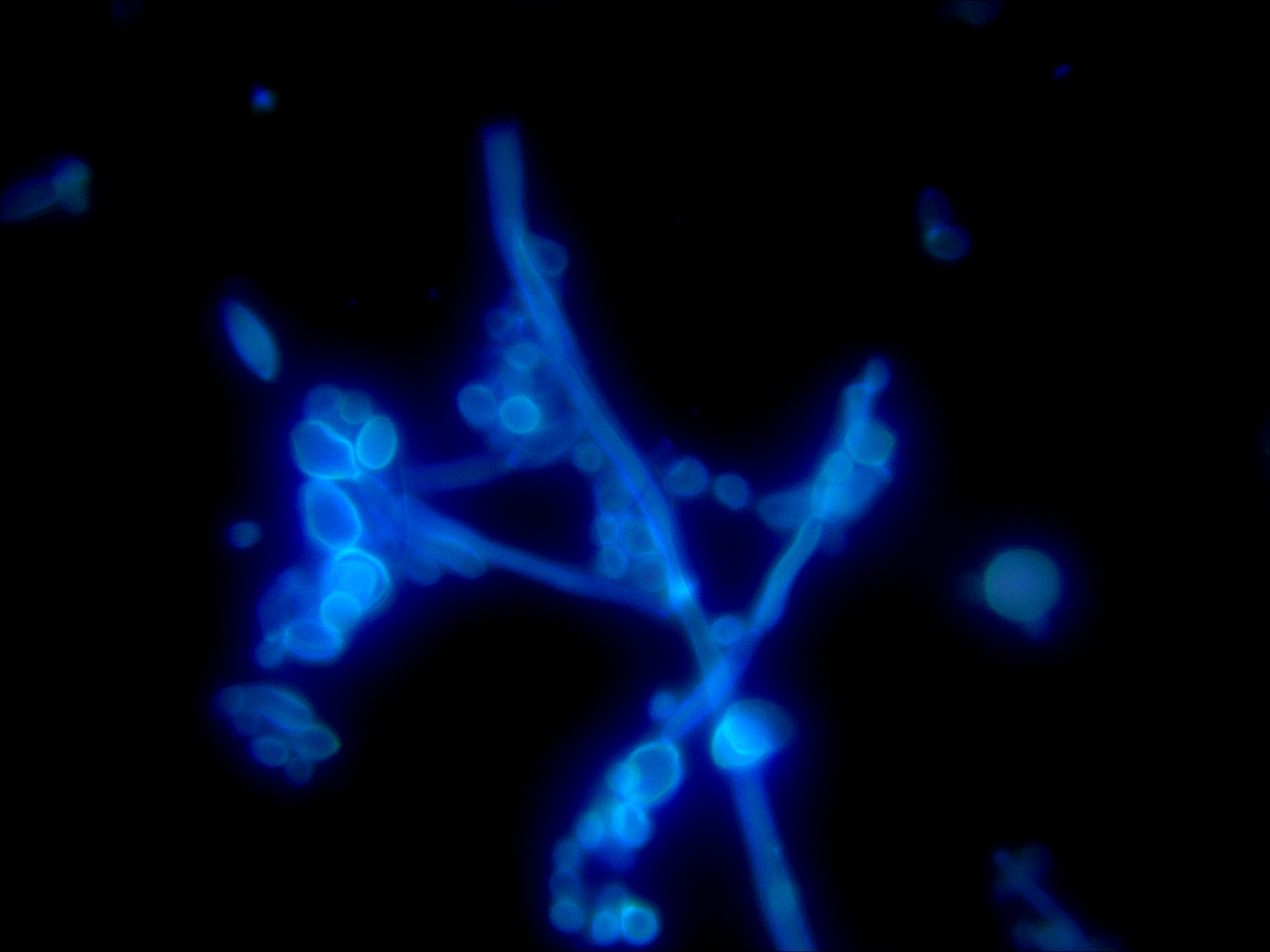
Candida magnified 400X Candida magnified 1000x
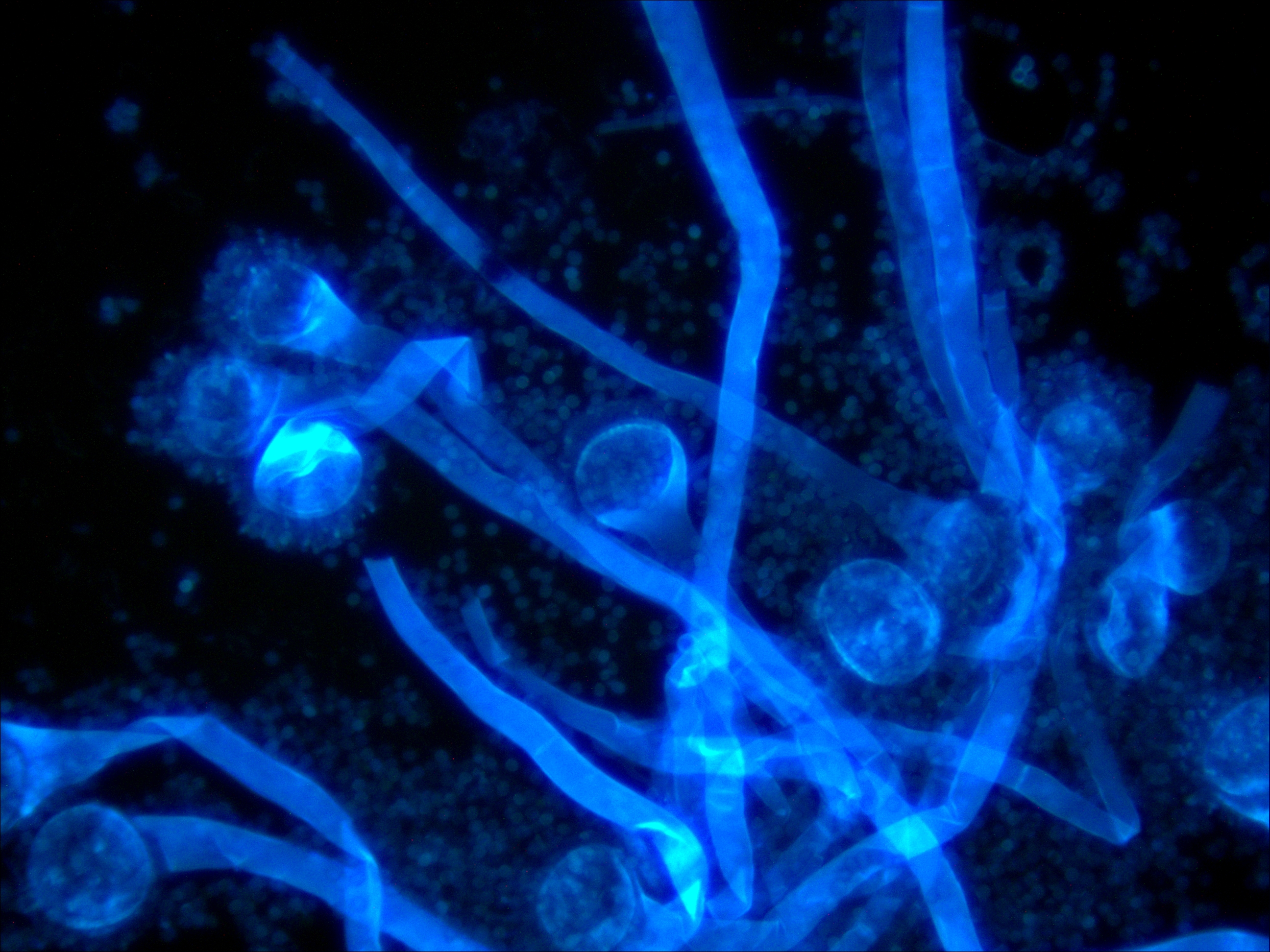
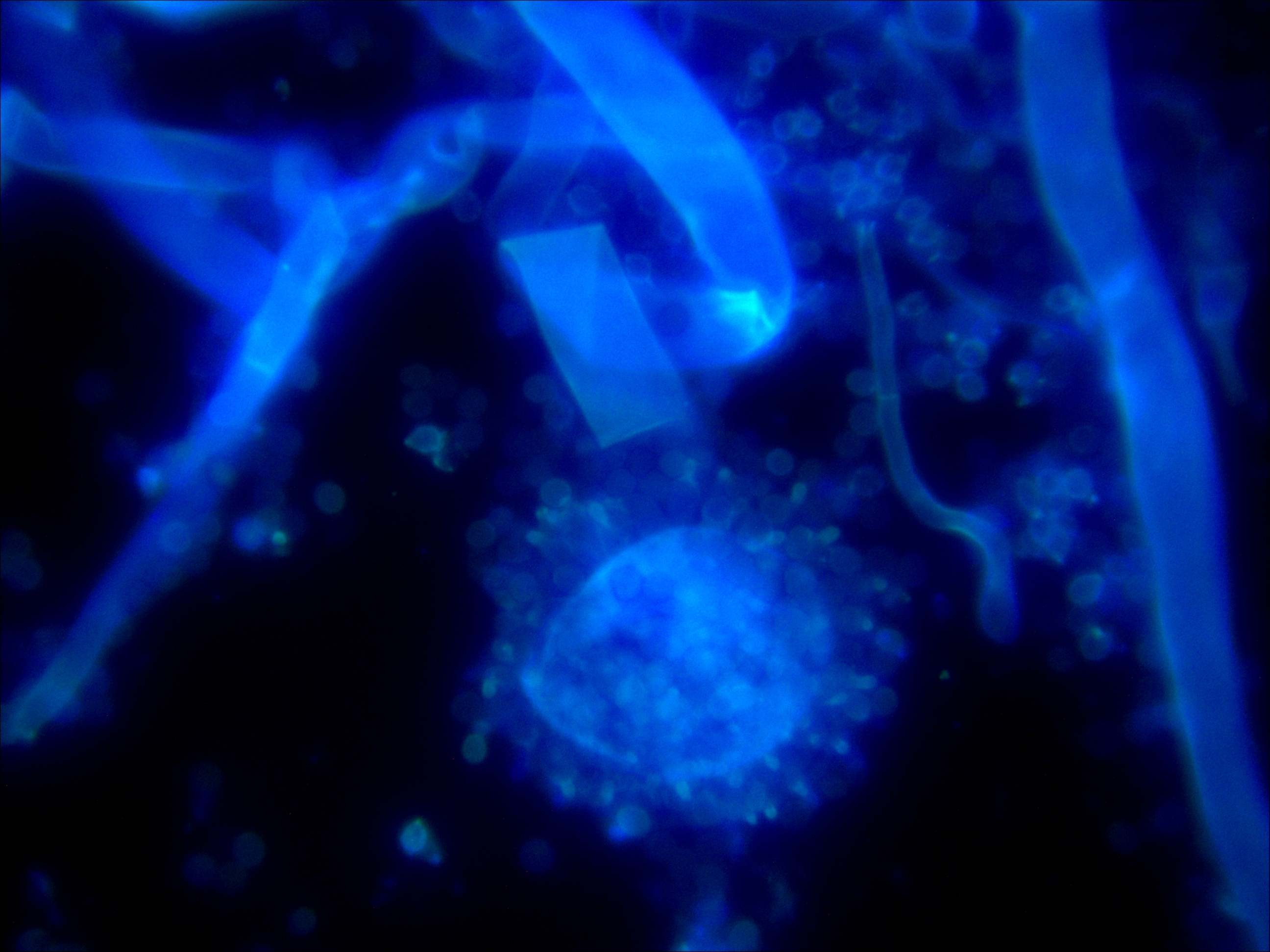
Aspergillus fumigatus 400X Aspergillus fumigatus 1000X
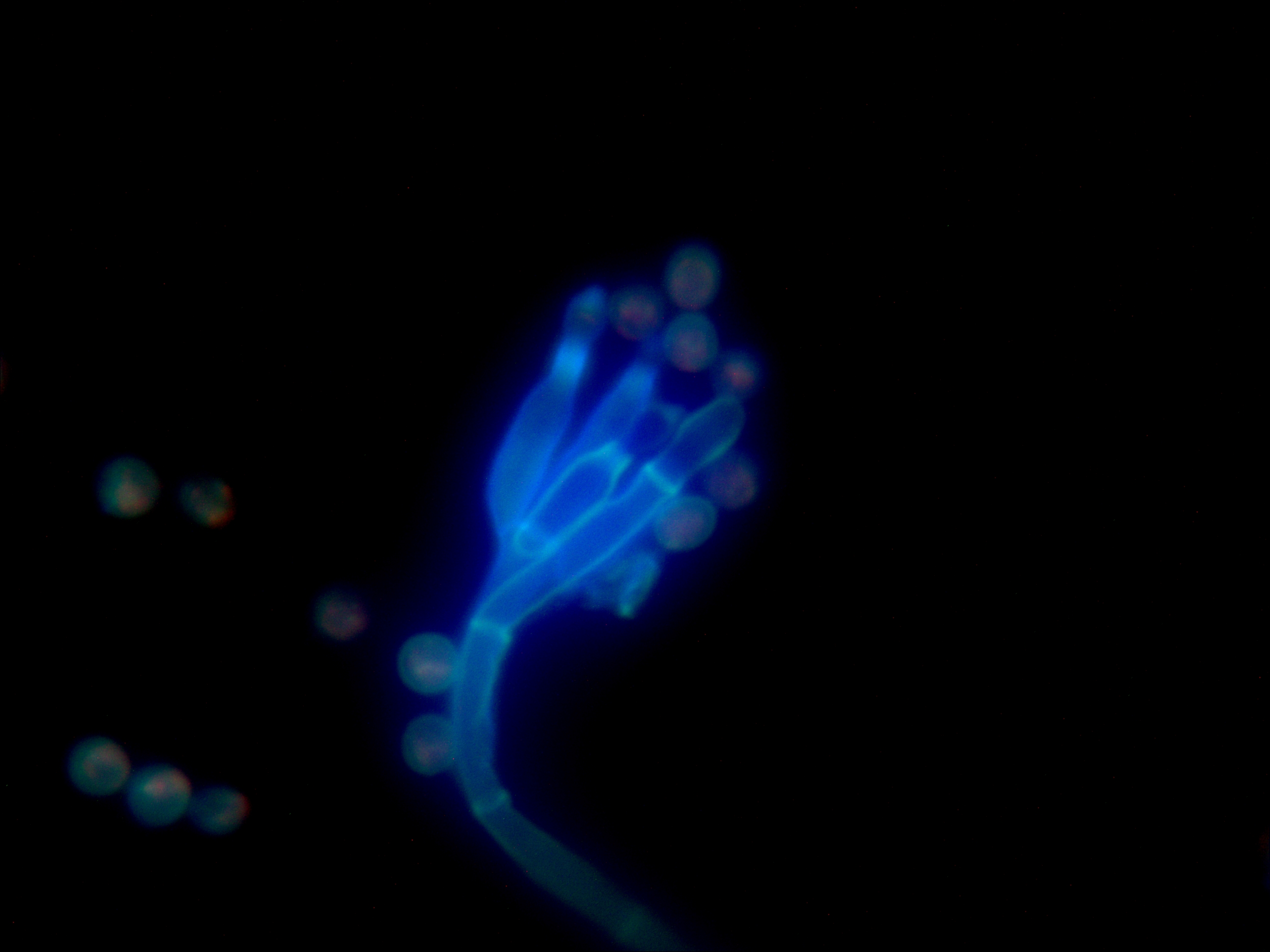
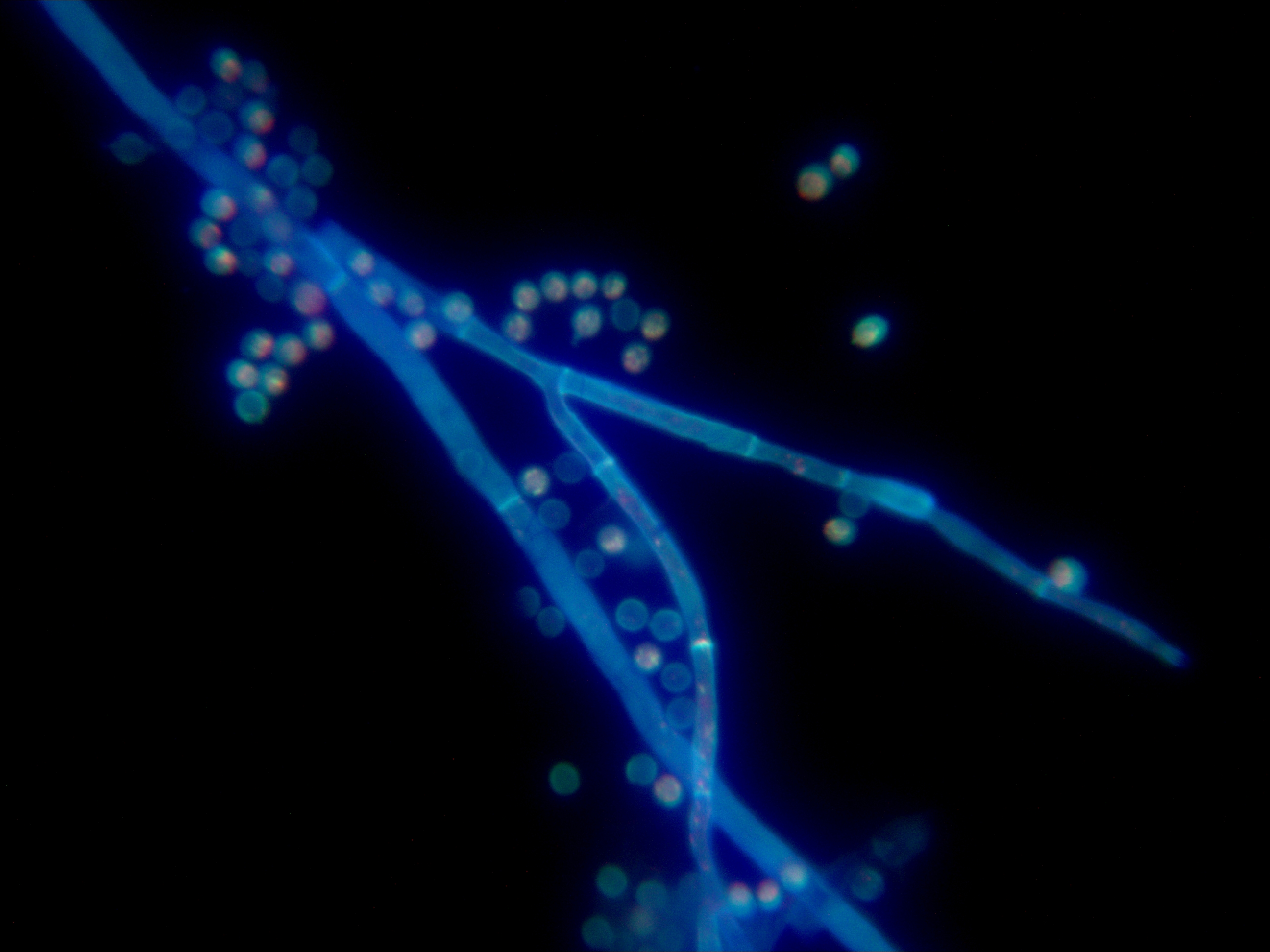

Aspergillus flavus 1000X Aspergillus flavus 1000X
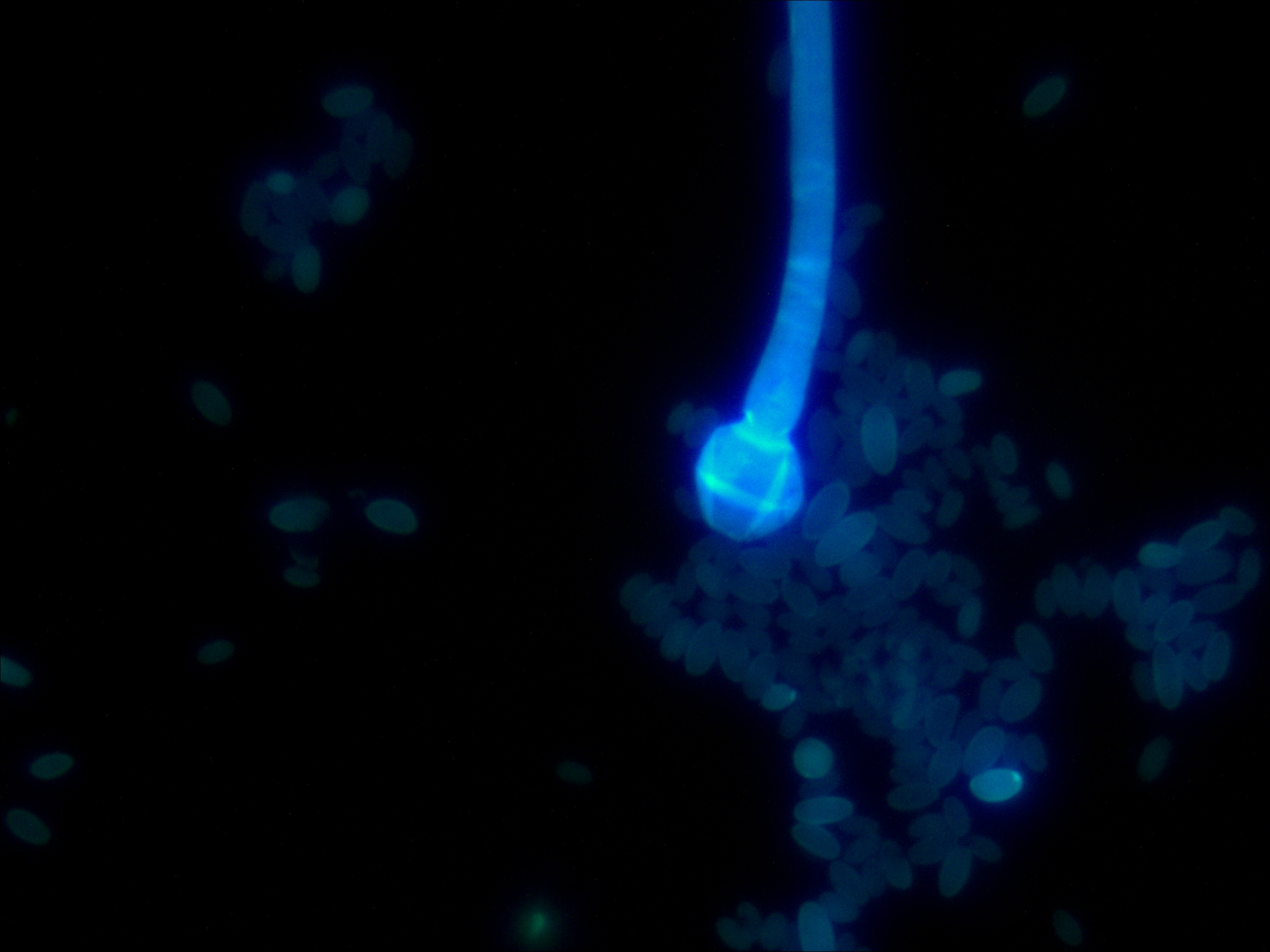
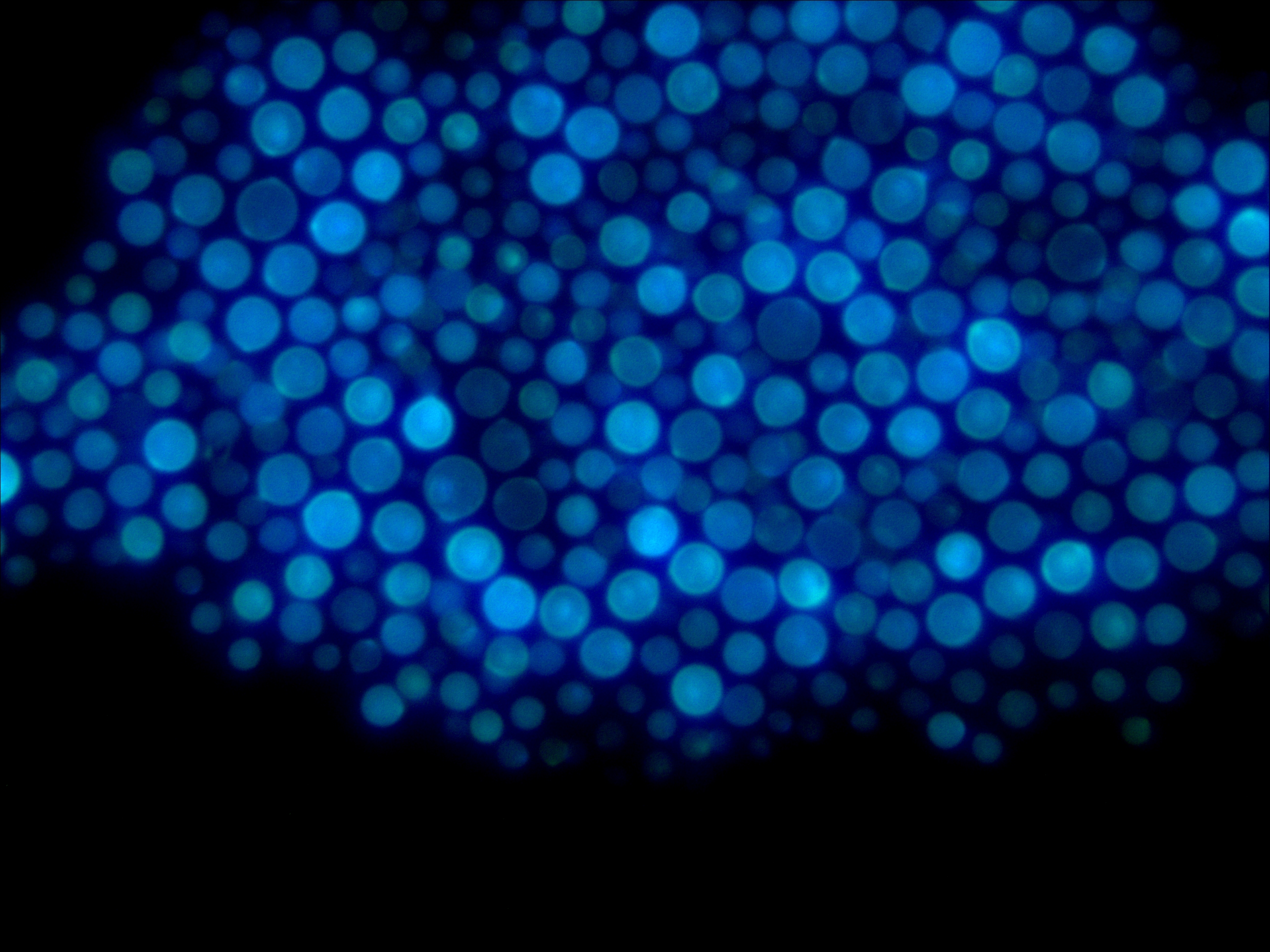
Rhizopus mutabilis Cryptococcus neoformans
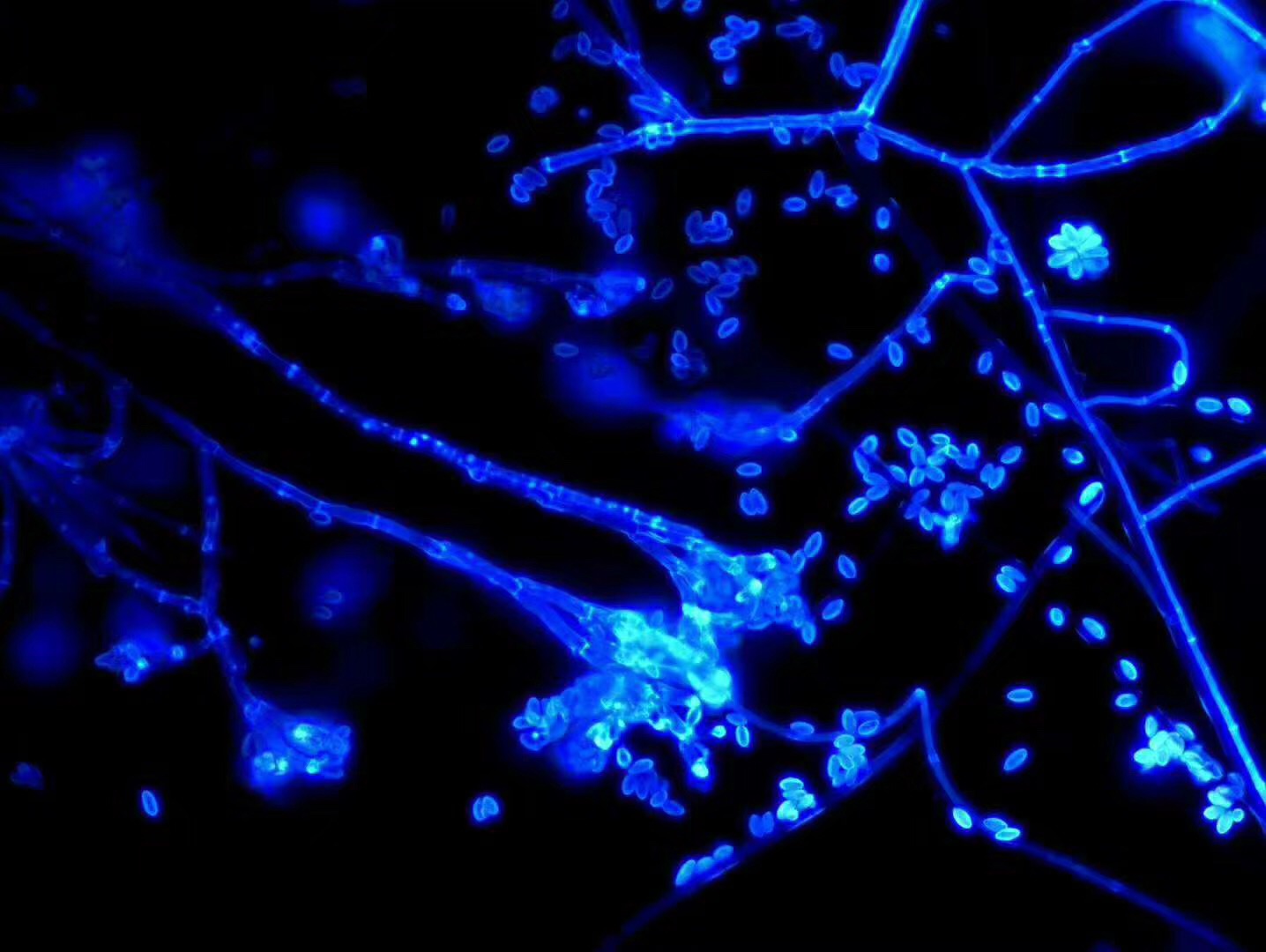
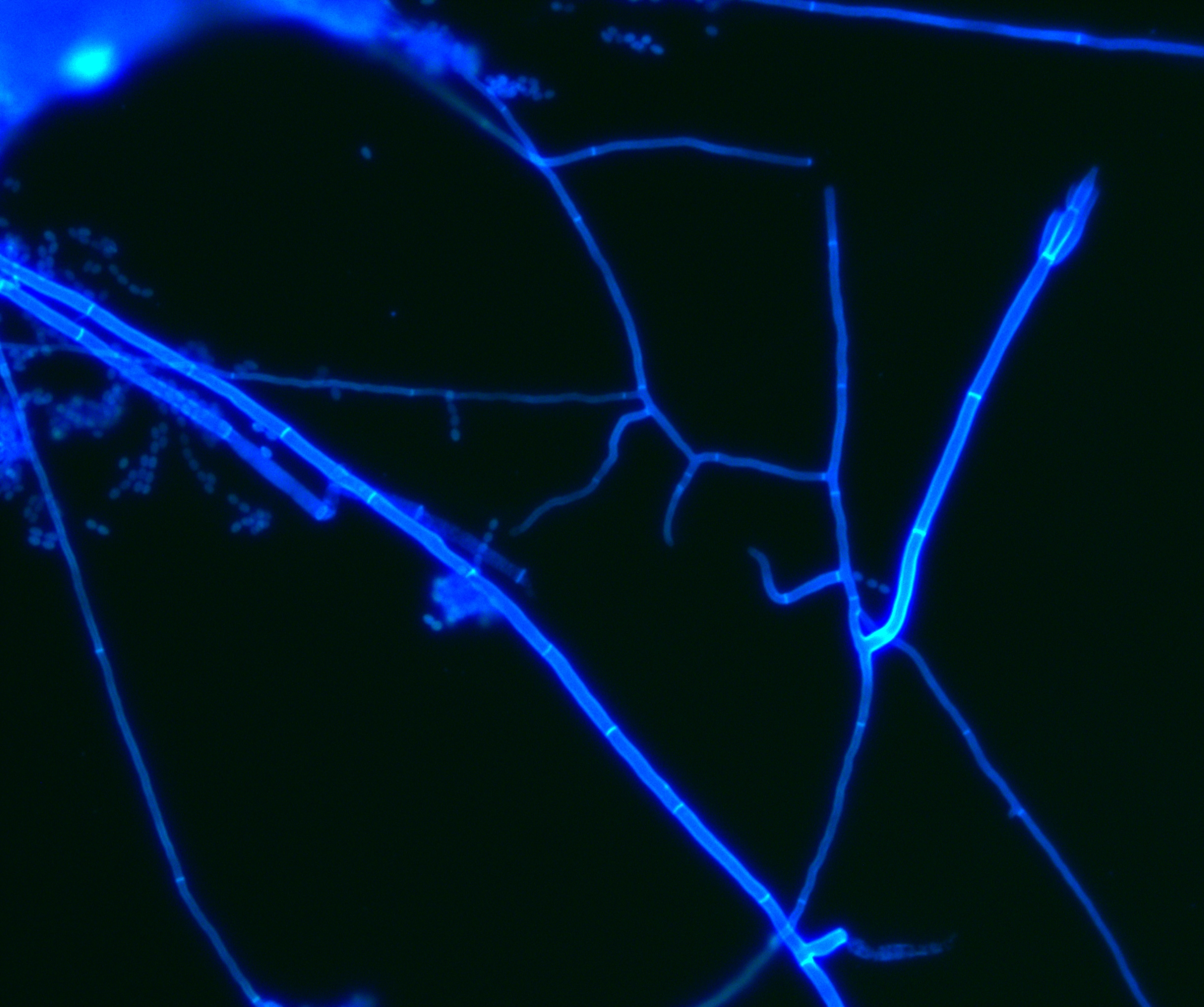
Fungi stained with BASO fungal reagent Staining of fungal hyphae with BASO fungal reagent
(BASO diagnostic reagent Baso Diagnostic Inc)